Data Subsystem¶
The data subsystem is optimized for the storage of large and small files, which can be accessed in a sequential or random fashion.
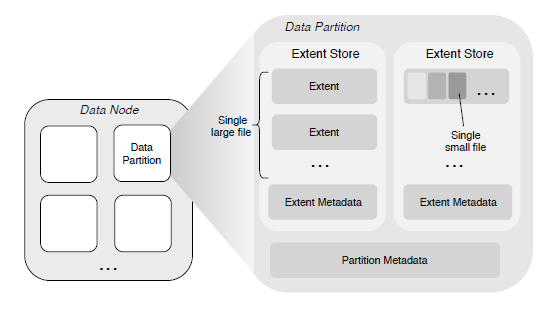
Features¶
- Large File Storage
For large files, the contents are stored as a sequence of one or multiple extents, which can be distributed across different data partitions on different data nodes. Writing a new file to the extent store always causes the data to be written at the zero-offset of a new extent, which eliminates the need for the offset within the extent. The last extent of a file does not need to fill up its size limit by padding (i.e., the extent does not have holes), and never stores the data from other files.
- Small File Storage
The contents of multiple small files are aggregated and stored in a single extent, and the physical offset of each file content in the extent is recorded in the corresponding meta node. ChubaoFS relies on the punch hole interface, textit{fallocate()}footnote{url{http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/fallocate.2.html}}, to textit{asynchronous} free the disk space occupied by the to-be-deleted file. The advantage of this design is to eliminate the need of implementing a garbage collection mechanism and therefore avoid to employ a mapping from logical offset to physical offset in an extent~cite{haystack}. Note that this is different from deleting large files, where the extents of the file can be removed directly from the disk.
Replication
The replication is performed in terms of partitions during file writes. Depending on the file write pattern, ChubaoFS adopts different replication strategies.
When a file is sequentially written into ChubaoFS, a primary-backup replication protocol is used to ensure the strong consistency with optimized IO throughput.
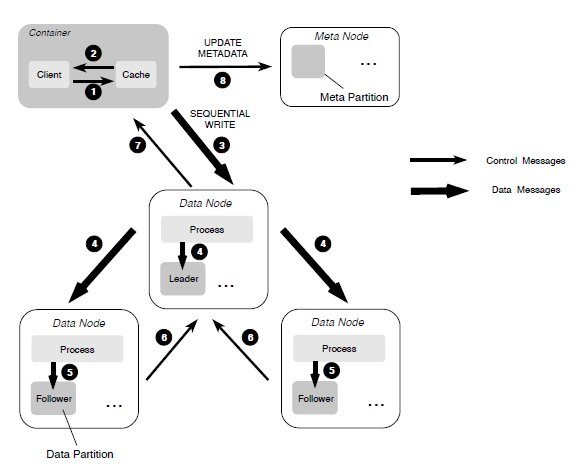
When overwriting an existing file portion during random writes, we employ a MultiRaft-based replication protocol, which is similar to the one used in the metadata subsystem, to ensure the strong consistency.
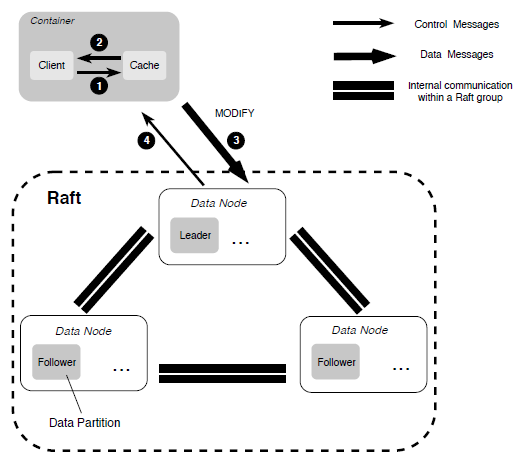
Failure Recovery
Because of the existence of two different replication protocols, when a failure on a replica is discovered, we first start the recovery process in the primary-backup-based replication by checking the length of each extent and making all extents aligned. Once this processed is finished, we then start the recovery process in our MultiRaft-based replication.
HTTP APIs¶
| API | Method | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| /disks | GET | N/A | Get disk list and informations. |
| /partitions | GET | N/A | Get parttion list and infomartions. |
| /partition | GET | partitionId[int] | Get detail of specified partition. |
| /extent | GET | partitionId[int]&extentId[int] | Get extent informations. |
| /stats | GET | N/A | Get status of the datanode. |